· LDI laser direct imaging technology: A Revolutionary Breakthrough in PCB Manufacturing
In the field of printed circuit board manufacturing, pattern transfer is one of the core processes. With the development of electronic devices towards lightweight and miniaturization, the precision requirements for PCB circuits are getting higher and higher. Traditional exposure techniques are no longer able to meet the demands of modern electronic manufacturing. Laser direct imaging technology emerged as The Times require and has become a key technology for high-precision PCB manufacturing.
01 Technical Overview
:What is LDI technology
LDI i.e,Laser Direct Imaging
This is a technology that uses the principle of direct laser imaging to project the line image directly onto the circuit board coated with photoresist in the form of a laser beam, thereby achieving pattern transfer.
Since Excellon launched its first argon laser imaging device, direct imaging technology has developed for over 40 years. The digital processes that initially achieved commercial success all utilized laser technology, while recent technologies have begun to adopt non-laser light sources such as light-emitting diodes.
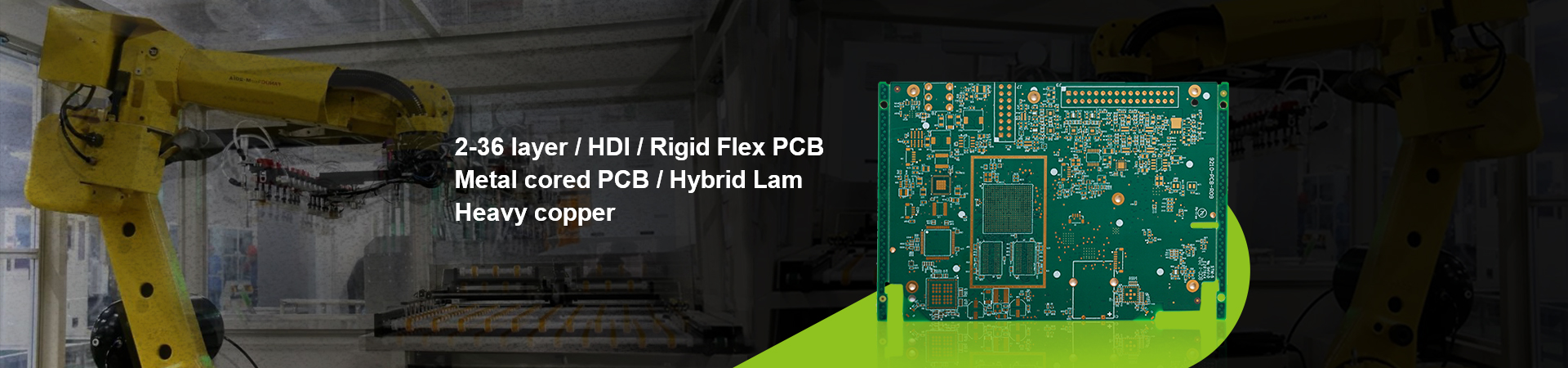
Unlike traditional exposure techniques that require a physical mask, LDI technology does not need a physical mask and directly forms circuit patterns on the photoresist through a laser beam
This not only eliminates the process of manufacturing and adjusting the film, but also significantly improves the accuracy and alignment ability of the graphic transfer.
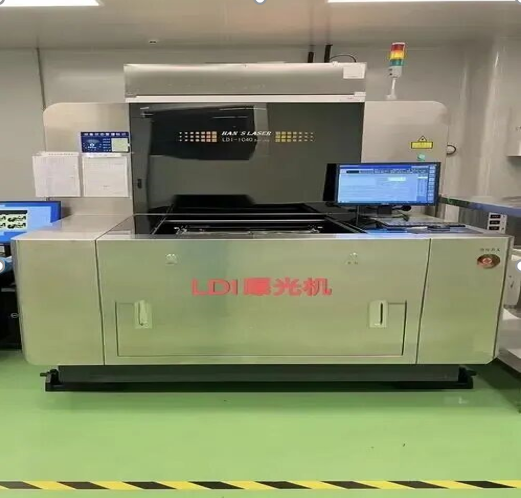

02 Working principle: How does a laser directly form an image
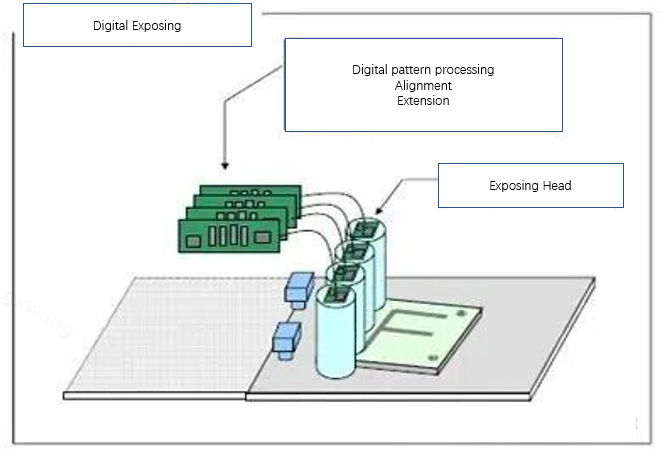
The working process of the LDI laser direct imaging system is quite precise. Its core lies in using digital graphic data to control the laser beam to be directly exposed on the working panel coated with photosensitive materials.
The system first receives CAD data from the design department, and then guides the laser beam to the working panel surface through a precise optical system.
Laser scanning systems often employ multi-sided mirrors or micro-mirror arrays (such as TI's DMD equipment) to control the direction of the laser beam.
During the imaging process, a low-power laser beam is generated through one or more laser diodes, with a wavelength of approximately 405nm.
These laser beams travel through complex optical paths and are ultimately precisely exposed in the form of pixels on the plate surface coated with photoresist.
The alignment system is one of the key components of LDI equipment. In a vacuum environment, the markers placed inside the operation platform start to form images at the positions of targets or holes at the bottom of the panel.
The CCD camera then aligns the fed working panel with the operation platform. After reversing the panel, repeat the same operation on the top of the panel.
This high-precision alignment mechanism enables LDI to achieve nearly perfect interlayer alignment, which is crucial for the production of high multi-layer and high-density interconnect boards.
03 Advantage comparison: The differences between LDI and traditional exposure techniques
Exposure method
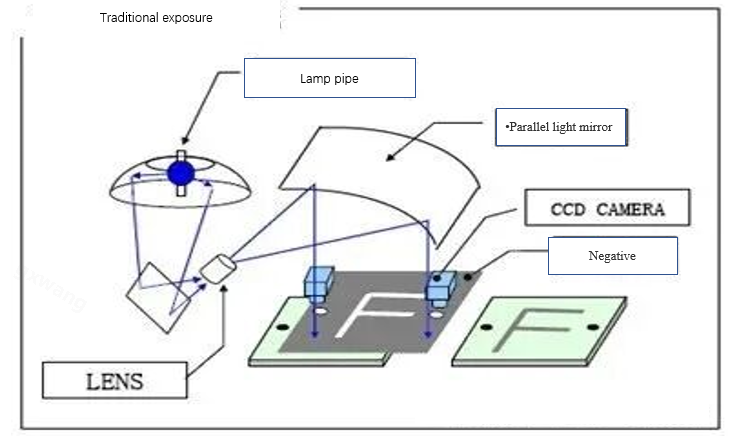
Compared with traditional exposure techniques, the most distinctive feature of LDI is that it does not use film, which is what is called "electronic film" and directly uses laser imaging.
The traditional use of film can cause many problems: poor dimensional stability and easy deformation and elongation; There is a limit to the number of times the negatives can be used. The production process requires changing the negatives and adjusting the alignment, which is quite time-consuming.
In actual production, it is quite common for 30 to 40 sets of film negatives to be replaced within 20 hours of operation. If each replacement takes 10 minutes, the time consumed would be 300 to 400 minutes, which amounts to 5 to 6.5 hours of the working day.
The replacement of pattern in an LDI system usually only takes a few dozen seconds.
Alignment ability
In terms of alignment accuracy, the LDI system demonstrates more obvious advantages.
Traditional exposure machines have limited alignment accuracy due to their reliance on manual alignment and solid negatives, especially in high multi-layer, high-density and buried blind hole plate parts, where the problem is more prominent.
LDI uses a visual system to automatically identify targets and, through precise calibration by a computer, can compensate for errors caused by material deformation, achieving alignment accuracy at the micrometer level.
Analytical ability
In terms of resolution capability, by adopting LDI exposure technology, the minimum line width/line spacing can be achieved at 1.8/1.8MIL.
However, due to the diffraction effect of light and the emission Angle of the lamp tube, traditional parallel exposure machines find it difficult to achieve such fine line analysis.
Cost-effectiveness
Although the initial investment in LDI equipment is relatively high, in the long run, it eliminates the costs of film production, maintenance and storage, reduces material waste and rework rate. Therefore, it has a significant cost advantage in small-batch and high mix production scenarios.
 Limitations of traditional exposure methods:
Limitations of traditional exposure methods:
1. Due to uneven illuminance, the line width near the edge has poor repeatability.
2. The film expands and contracts, and the alignment accuracy is problematic. For a 500mm board, there can be an error of several hundred micrometers. When high precision is required, it leads to low yield and yield. Advantages of LDI exposure method: 1. Shorten the cycle (reduce the film process for direct imaging) 2. Improve quality (contactless, uniform energy, high alignment accuracy)
3. Save costs (No need for film negatives, use virtual electronic film, improve quality)
04 Key control points: Ensure the imaging quality of LDI
To ensure the imaging quality of LDI, the following key points must be strictly controlled:
Laser energy control is the core of the LDI process. The stability of laser energy directly affects the exposure effect and the accuracy of line width.
Low energy can lead to insufficient exposure of the resist and incomplete patterns. Excessive energy may lead to line width deviation or even damage the material.
The laser power needs to be calibrated regularly to ensure that the energy output is stable within the process window.
Precise alignment is another key aspect of LDI technology. The LDI system uses a high-resolution CCD camera to capture the alignment marks on the board surface and calculates the scaling, rotation and displacement parameters through algorithms to achieve precise pattern alignment.
For warped working Panel, the system also needs to have a three-dimensional surface compensation function to ensure the uniformity of focusing at different positions.
Environmental control cannot be ignored either. Changes in temperature and humidity can affect the dimensional stability of materials, and thereby influence the imaging accuracy.
The working environment of LDI should be maintained at a constant temperature and humidity, with the temperature controlled at 22±2℃ and the relative humidity kept between 50% and 60%.
Material compatibility is an often overlooked but crucial factor. LDI requires the use of dedicated LDI-type dry films and LDI-type inks, which have high sensitivity to specific wavelengths used in LDI, such as 405nm.
Special materials: Requirements for LDI type dry film and ink
With the popularization of LDI technology, the development of specialized materials is also becoming increasingly important. Unlike traditional UV exposure, LDI uses high-energy, single-wavelength laser light sources, which requires that the photosensitive material must match the laser wavelength.
The dry film dedicated to LDI needs to have characteristics such as high sensitivity, high resolution, and high adhesion.
The FD series developed by leading companies is a new type of water-soluble dry film specifically designed for laser direct imaging. It features high sensitivity, high resolution, high adhesion, and rapid film removal.
The digital photoresist materials developed by the Institute of Materials and Chemical Engineering of the Industrial Technology Research Institute focus on the 403 nm photosensitive band and high resolution as the key technical layout points.
In the structural design of high-sensitivity photo sensitivities, they introduced functional groups suitable for the DLT photosensitive band to control the light absorption band. At the same time, they developed new photosensitive resin synthesis technology and photoresist formula technology, thereby enhancing the sensitivity and resolution of photoresist materials.
The formula of LDI-specific solder mask ink also needs to be optimized to adapt to laser exposure. Compared with traditional solder mask inks, LDI type inks should have a higher absorption efficiency at the laser wavelength while maintaining excellent developability and chemical resistance.
The materials developed by the Institute of Materials and Chemical Engineering of the Industrial Technology Research Institute have a high exposure dose <20 mJ/cm². Under the condition of 20 mJ/cm², the line width after development can reach 2.5 μm, and the variation of the photoresist line width is less than 5%.
The development of these specialized materials enables LDI technology to achieve its maximum efficiency in PCB circuit formation, solder mask patterning and other processes, meeting the manufacturing requirements of fine circuits and small-pitch electronic products.
Address:3-401, Dahong Technology Innovation Park, Xinyu Road, Shajing Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen
Q Q:172750477